Never heard of the word CDN (content delivery network), don’t worry. I will explain what exactly a CDN is, how it works and do you require a CDN for your website. By the end of this article, all these questions will be answered in complete detail, and you will finally know that is CDN suitable for you or not.
Picture courtesy of Wikipedia.
What exactly is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
First of all, I will explain what a CDN is; the acronym stands for Content delivery service, is a highly distributed network which is known as the transparent backbone of the internet. It is a platform of high optimized servers which deliver content that includes streaming media and web applications. You may not know, but almost everyone over the internet has interacted with CDNs either they know it or not.
We do it while watching videos on youtube, downloading applications, reading articles, scrolling through your newsfeed at social media platforms or shopping online. It does not matter what kind of content you consume over the internet that maybe every pixel image, every movie frame, every character of a text you see, will most probably have a CDN linked to it.
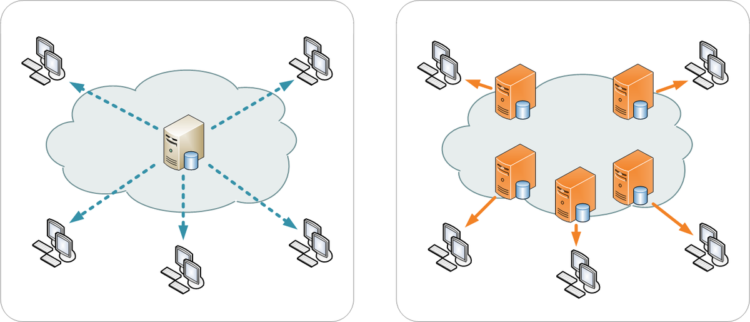
Now let me you explain to you what is a CDN in technical terms. It is a system of highly distributed servers that delivers the web pages and the other web content to a particular user based on his geographical location from the origin server which is probably far away from the user who requests the web pages. This network of servers is spread across geographic and network locations. CDN acts as a mediator between the origin server and the user, delivering fast and secure media to all users.
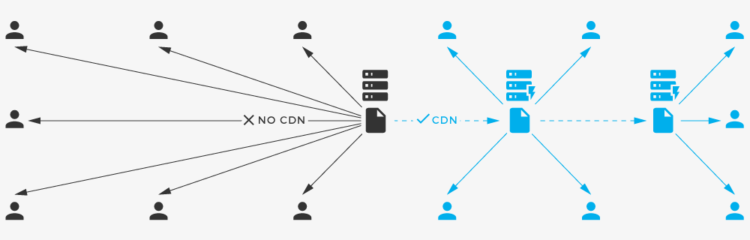
Things will run at a much slower rate without a CDN, that is the origin server must respond to every individual end user request. Thus resulting is substantial traffic to the origin and significant load, hence increasing the rate of origin failure, leading to a server crash, if traffic spikes are increasingly high or if the load is insistent.
CDN usually delivers static content which is images, HTML, CSS, and javascript. CDN also provides content such as 4K and HD-quality video, software downloads such as apps, audio streams, OS updates and also data records that contain financial and medical information and much more. Almost any data that can be digitalized is delivered through CDN.
CDNs are designed to resolve one major issue, that is the problem of latency. Latency is the irritating delay that occurs right from the moment you request to load a web page to the very moment until its content appears on the screen.
The delay interval is usually affected by many factors, but the primary cause is always the distance, that is the distance between you and the website’s hosting server. A CDN’s primary goal is to shorten this physical distance which is virtual and to improve the site’s performance, speed and it’s rendering.
Courtesy of CDN reviews.
How a Content Delivery Network (CDN) functions.
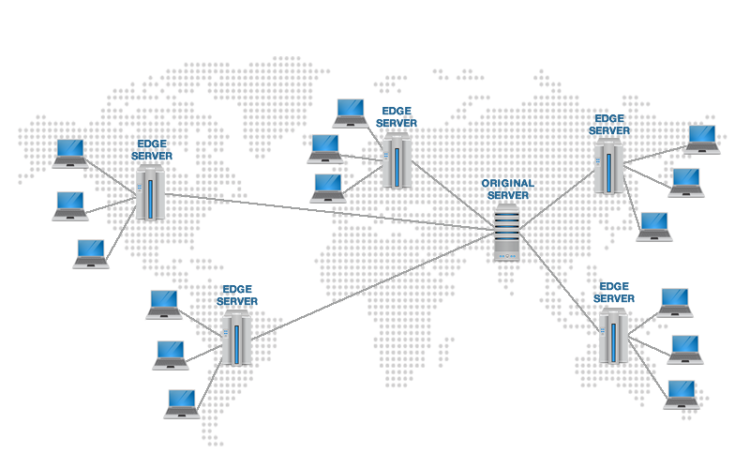
A CDN stores a cached version of primarily static data in multiple geographic locations knows as (points of presence or PoPs) to reduce the distance between the end user and your website’s server. Each PoP contains multiple caching servers that are responsible for content delivery to all the visitors within its proximity. To simply explain the functionality of a CDN let me give you an example.
Let’s say you have a WordPress blog and usually when a user visits your blog, they are redirected to your web host’s server that is located in Los Angeles, California. So every end user is accessing your website to view it through this one server, but if you have high volume traffic of then, there is a chance it may overload your server which may result in slow loading of the site and even leading to a complete server crash.
This is where CDN will play its part as it is a network of multiple servers which most importantly are dispersed across the world and when you use a CDN, all your cached static content is stored on all of these servers. Now when a user visits your website( original server), the CDN technology at once redirects them to the nearest server to their location.
If you have a server in California and someone from Amsterdam tries to visit your site, then they will be redirected to the nearest server close to London. This will result in limiting the number of internet hops which is needed to transmit the static content to your end user. All in all, the closer your CDN server is to your user, the faster it will load the web pages on the user’s screen.
Courtesy of StackPath Blog
Do you need a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for your website?
In today’s age speed isn’t a luxury but it is a necessity, all it takes is 3 seconds for you to lose your 50% website, viewers. That is proven by a research some years ago that a loading time a mere 3 seconds leads up to a 50 percent increase in bounce rate and 22 percent fewer conversions than a loading time of only one, making speed a vital factor for all people over the internet. Even the giants like Amazon discovered that every 100 ms of page load time led to a drastic decrease in sales.
The importance of speed has proven benefits in SEO ranking as Google highly ranks the websites that are well optimized and running smoothly. SEO genius Brian Dean has listed “speed” as one of the top ten ranking factors. So how to maximize speed, if you’re on a small scale then compressing images, optimizing visuals and minimizing on-page components will be effective. But if you’re a giant and have high international traffic on your website then there is one solution which has proven and sustainable results that is, getting yourself a CDN.
Now that you have understood almost everything there is to about CDNs, I have a list questions for you, which you should ask yourself in determining whether a CDN is a right choice for you or not.
- What is the geographic diversity of your audience?
If the traffic on your website is local, then there is no need to deploy a CDN, but if you have high international traffic, then you will certainly need a CDN. Understanding the geographic location will help you in choosing that whether you need a CDN or not.
- What is your current load time?
There are free tools available that can answer this questions immediately. WebPage TEST is a free tool which provides a detail waterfall chart that breaks download time per content, and it also suggests improvements. If your page has a slow load time, then you need a CDN.
- How good is your website at handling traffic surges?
If your website malfunctions during surges in traffic then you certainly need a CDN.
- How much traffic does your site receive?
The amount of bandwidth that you use is indeed a crucial factor. The higher the traffic, the more severe need is of a CDN.
- What is the overall experience of the users?
For that, you need to evaluate your website both qualitatively and quantitively but if you truly need to assess your site then who better than to ask the users who frequently visit your site, ask them for their feedbacks about what needs to be improved and what’s functioning properly.
Conclusion
CDN has now become a necessity rather than a luxury, especially for those people who deal in huge online businesses like retail, finance, healthcare, etc. If you own such online business, then you need a CDN to grow your business further, and you don’t have to worry, as it is the age of digitalization you can easily get a “cheap cdn” and with it, you can push your online business to new heights.
Content provided by Max Grayman, marketing manager of spacecdn.com